Unix-an Overview
-INTRODUCTION OF UNIX -USES OF UNIX -HISTORY -IMPORTANT UNIX COMMANDS
INTRODUCTION OF UNIX
WHAT IS UNIX
- It's a family of operating systems - MacOS , Android , iOS , Linux etc.
- Windows is one of the main operating systems that doesn’t belong to unix OS family .
As a developer you will need to learn some basic Unix commands to do variety of opertions.
Unix OS
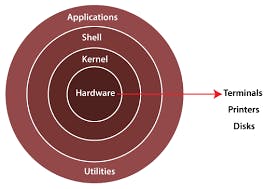
shell
The shell is the interface between the user and the kernel.
- It accepts and interprets commands through a command line interface (CLI) , also called terminal.
- There are many types of shell -
- BASH - Bourne again shell.
- C shell etc.
USES OF UNIX
- Multi-tasking. Unix is designed for high-performance computing. ...
- A backbone of modern technologies. ...
- Impactful towards other OS. ...
- An invention of Linux. ...
- A host of services. ...
- Command-line functionality. ...
- Text-based processes. ...
- Regular Expression.
HISTORY
The history of Unix dates back to the mid-1960s when the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, AT&T Bell Labs, and General Electric were jointly developing an experimental time-sharing operating system called Multics for the GE-645 mainframe. Multics introduced many innovations, but had many problems. -Default; user interface: Command-line interface & Graphical (X Window System).
-Developers : Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna at Bell Labs.
-Initial release: 1969; 52 years ago.
-License: Proprietary.
-OS family : Unix.
-Source model: Historically closed source, now some Unix projects (BSD family and Illumos) are open sourced.
-Written in: C and Assembly language.
IMPORTANT UNIX COMMANDS
- echo (text): To print text on the terminal screen.
- clear: To clear the terminal screen.
- exit: To exit the terminal.
- pwd: Present working directory.
- ls: it list all the stuff inside this particular directory.
- cd: change directory means to enter the child directory from a parent directory.
- cd ..: To go back in parent directory i.e . a step back.
- man: used to display manual for any command.
- ls -l: It shows a list of stuff along with all information such as file permission information , file, size, date and time it was created , number of files inside it, and name of the files.
- ls -a: It also shows a list similar to "ls -l" command but it also show the hidden files.
- ls -s: To display a list of stuff sorted by the size.
- ls -r: To display a list of stuff in reverse order.
- touch: To create a new file.
- echo "text" >> file.txt: To update a line in the file.
- head (file.txt): To show the top 10 line of the file.
- tail (file.txt): To show the bottom 10 line of the file.
- cat (file.txt): To display the file on the terminal screen.
- nano (file.txt): To open the editor window for the file.
- grep: To find the string in the file.
- grep -n: To find the sting along with the line number in the file.
- mkdir: To make a new directory.
- rm: used to delete the file.
- rmdir: used to delete the empty directory.
- rm -r: To delete any folder.
- mv (old name) (new name): used to rename the folder.
- cp (source) (destination): to copy the file.
IMPORTANT SHORTCUT KEY
- Ctrl+C : copy text.
- Ctrl+V : paste text.
- Ctrl+X : cut text.
- Ctrl+Z : undo.
- Ctrl+Alt+T : open terminal.
- Ctrl+Alt+D : show desktop.
- Alt+Tab : switch Tab.
- Ctrl+W : close window.
- Ctrl+X : exit from editor window.
- Ctrl+Z : To come out of any command in terminal.
- Ctrl+C : To came out of any command in terminal.
- Ctrl+Shift+C : copy from terminal.
- Ctrl+Shift+V : paste in terminal.
